Anaconda, the Fedora system installer, is probably the best installation program available on any Linux or BSD distribution, and the version that comes with Fedora 16, version 16.25, has a couple of visible enhancements that make it even better. One of those enhancements is support for GPT disk partitions. GPT, or GUID Partition Table, is an alternate partition scheme that eliminates the restrictions of the MBR or Master Boot Record partitioning scheme.
With GPT, partitions sizes greater that 2 TB are possible, and more than four primary partitions can be created. Those are two major shortcomings of the MBR partitioning scheme. In Fedora 16, Anaconda defaults to GPT in standalone installations. However, when the target disk has an existing installation of another distribution, it creates MBR partitions, if that is what the existing OS is using.
Fedora offers several installation images for download – Live CD, DVD, network install, and bfo. Regardless of the installation image used, you will be using the same version of Anaconda. It can install to both local and remote storage devices. If you are installing to a local disk, which most users will be doing, you will be choosing the selected option shown in the image below.

Anaconda offers many automated disk partitioning options, which, by default, create partitions based on LVM, the Linux Logical Volume Manager. LVM is still the default in Anaconda 16.25, but a new feature makes it possible to create automated partitions that are not based on LVM. So, if you wanted to install Fedora 16 on non-LVM partitions, just disable the “Use LVM” option.

This screenshot shows the partitions created when the “Use LVM” option is left enabled. While everything looks good here, there is one minor issue: The disk space allocated to the root Logical Volume is far more than is needed to install the system. That goes against the rule of thumb that governs setting up an LVM-based system. But if you want to install Fedora 16 on an LVM file system, you do not have to create the partitions manually; just let Anaconda create them, then edit the partitions that get more space than they actually need. For example, to reduce the space allocated to lv_root in this screenshot, double-click it, or select it and click the Edit button.

That should open this window. The values shown are the defaults. A new installation of Fedora 16 uses about 4 GB of disk space, so clearly, 51200 MB (51 GB) is too much. Another parameter you can modify here is the “Logical Volume Name.”

This is the same window showing the modified values

After reducing the disk space allocated to the root logical volume, there is now free space that can be used to create extra logical volumes or extend or grow one that runs out of space. Unless you know what to look for, you would not know that the partition in this screenshot are GPT partitions, which is the default in all standalone installations of Fedora 16. When there are four primary partitions or less, and the first primary partition has “BIOS Boot” in the Type (File system column), then you know that GPT is in use. The size of the “BIOS Boot” partition, usually 1 MB, is another tell-tale sign.

If you opt not to use LVM, Anaconda creates the partitions shown in this image. Here, it is obvious that they are GPT partitions because there are five primary partitions. Note that under GPT, the first partition is the “BIOS Boot” (bios_boot) partition. As with the LVM partitions, too much disk space is allocated to the root partition, but you can also reduce it without resorting to manually creating all the partitions.

This is the editing window with the default values.

And this is what it looks like after modification.

Now, you have free space to create other GPT partitions. Keep in mind that installing Fedora 16 on non-LVM partitions does not have any advantages over an LVM-based system, so it is always a good idea to use the default, that is, leave “Use LVM” enabled.


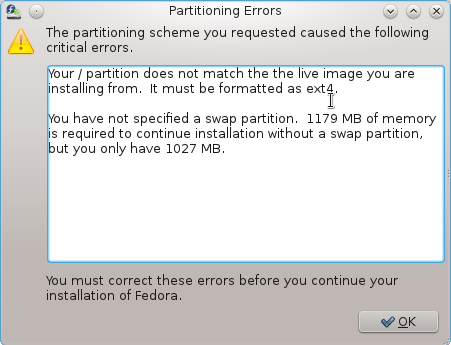




Thanks for writing this article, it’s nicely done and almost entirely correct. However, it’s not true to say that “Apparently, it will not because the Live CD editions of Fedora 16 do not support creating anything other than the default LVM partitioning scheme.” The live installer is restricted, but not that restricted. The restriction is that the root partition (in fact, any partitions which contain files from the actual system image, so if you were to split out /usr or /var, for e.g., the restriction would apply to those too) must be ext4. You can create a partition layout manually, have the sizes be whatever you want, use LVM or not, use encryption or not – but the partitions with system files on must be ext4. The reason is simple: Fedora live images are actually compressed snapshots of an ext4 filesystem, and the live installation process does not take actual .rpm package files from a disc or repository and install them one by one, as the ‘traditional’ installer does, it just essentially writes the filesystem image directly onto the disk. To do this, the target filesystem(s) have to be the same as the source, i.e., ext4. You can’t write an ext4 filesystem image to a btrfs partition.
Who cares? If it is a server you reboot it once ayera or less. If ir is a desktop you suspend it and only power it off when you are leaving for a week or so. And anyway even if using systemd activating LVM is only a small part of boot time.
About people saying LVM is slower, it is like peole saying you should compare your own kernel: none of them has bothered running a benchmark. Now, logically LVM should be slower or at least use more CPU time. It doesn’t. Now if you think at it the overhead for finding the right block is something in the order of a couple dozens of CPU cycles. Also my LV was in pristine condition: if it is fragmented due to having ben extended multiple times then it _will_ be slower than a partition because there will be head movements but of course the point is moot because the partition would have become full and if you were able to carve a new one then you could have done the same thing with LVM.
Also there is a nice thing with LVM: you can give them significanty names so you don’t need neither mounting them nor running a special tool (for reading labels) to know what you have stored in them.
I personally have used LVM since it became the default in Fedora. And yes, its flexibility helped me considerably (and this is why I kept using it).
Anyway, searched a little and it seems that you are right that LVM doesn’t degrade performance much by itself.
I’m going to agree with your Anaconda… statement with one small hiccup – Time Zone selection is very finicky due to the small size of the world map.
True. I wish they will use the same system employed by Ubuntu.
Non-LVM partitioning has an advantage over LVM method: speed…
I benchmarked LVM vs non-LVM on the same physical partition and there was no difference.
I have not compared it myself but I have read it in many places. Even in the case you mentioned, it is *possible* to achieve higher boot speeds if you don’t use LVM (you’ll need to disable some services running at boot by systemd).
Are these “higher” (faster) boot speeds really that much? At best, are we not talking no more than 2 or 3 seconds here? The benefits of LVM far outweigh that reduced boot time.
Well, apparently it could be around 8 seconds for a machine: http://lists.fedoraproject.org/pipermail/devel/2011-October/157732.html
But yes, LVM benefits might outweigh the gains.