Pardus is a desktop-oriented, Linux distribution. The latest release is Pardus 2009.1, and just like Pardus 2009, it comes with IPTables/Netfilter, the firewall application built in to the Linux kernel, disabled. This is a short tutorial showing how to enable the firewall via the graphical firewall manager, and tweak the configuration options available.
Pardus is a desktop-oriented, Linux distribution. The latest release is Pardus 2009.1, and just like Pardus 2009, it comes with IPTables/Netfilter, the firewall application built in to the Linux kernel, disabled. This is a short tutorial showing how to enable the firewall via the graphical firewall manager, and tweak the configuration options available.
It’s always better, whether there are open ports or not, to have IPTables/Netfilter running out of the box. However, distros like Pardus opt to have the firewall disabled. Don’t know why, but that’s just the way it is with some of these distros.
Like all its graphical management tools, Pardus comes with a custom developed graphical firewall manager. The first step is to launch the graphical firewall manager from Menu > Application > System > Firewall Manager.
This is Pardus’s graphical Firewall Manager in the default state – disabled. Click on the “Start” button to activate or enable it.
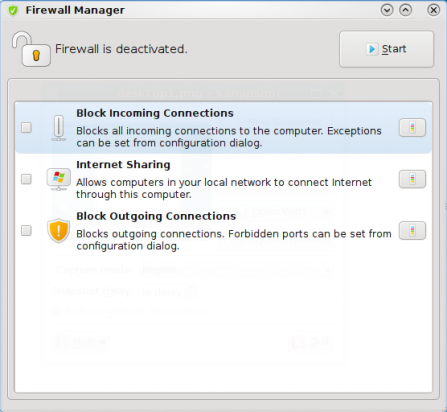
Firewall Manager in the default status - disabled.
Firewall Manager in the enabled state
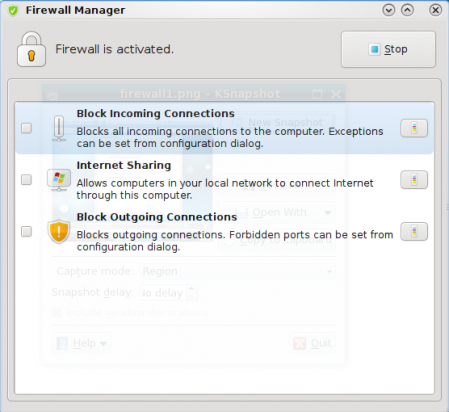
Firewall Manager in the enabled state.
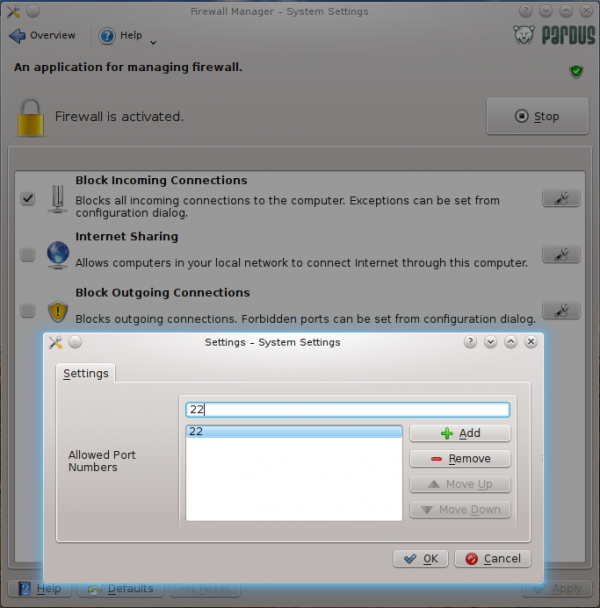
Once enabled there are three configuration options available. If you choose to block all incoming connections, and then decide to allow specific connections through, Firewall Manager allows connection blocking to port numbers. While this is good, it would have been even better to also have the ability to block connections from specific hosts or networks.
Incoming connection blocking
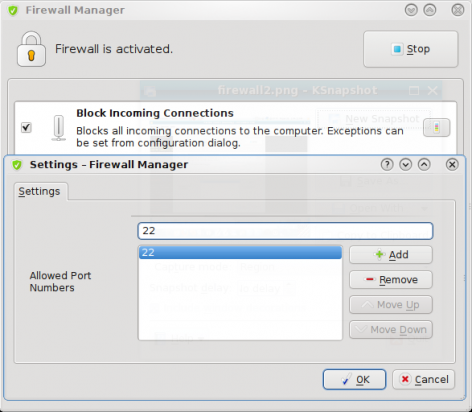
Firewall Manager showing how to block incoming connections
The second option allows you to share your connection, that is, configure the computer as a gateway for other computers in your LAN. Again, there is no fine-grained control. You can’t deny access to a specific host within your network, or specify time-access controls.
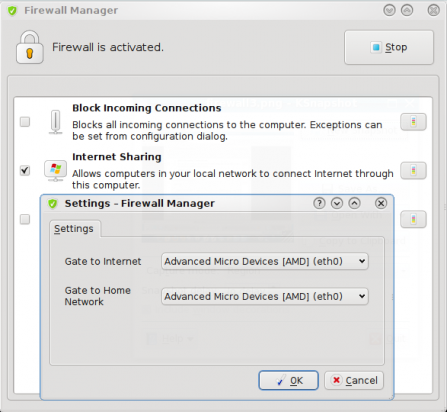
Configuring connection sharing
The last option allows you to block outgoing connections. And you can only forbid outgoing connections by port numbers. When I tried this feature, I found that just enabling outgoing connection blocking and closing the window, does not actually block any outgoing connections. To stop Web browsing, for example, you will have to specify port 80 ( the default HTTP port) as shown in the screenshot below. Note that this will only block Web browsing to Web servers listening on that specific port. Other forms of network access will still go through. Keep in mind that this is only my experience with this application. There is no documentation showing how you can do tweak this feature, so this is what you would experience as a first-time user.
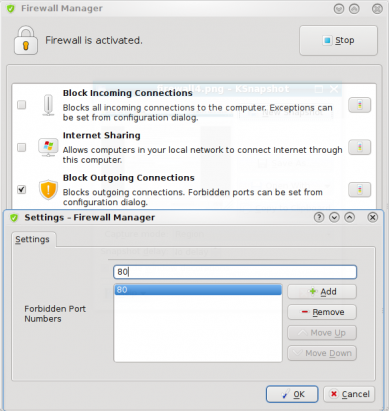
Outgoing connection may be blocked via the Firewall Manager
Pardus’s graphical firewall manager has a very simple and clean interface, and it’s also very intuitive to use. It’s, however, lacking in advanced configuration features.