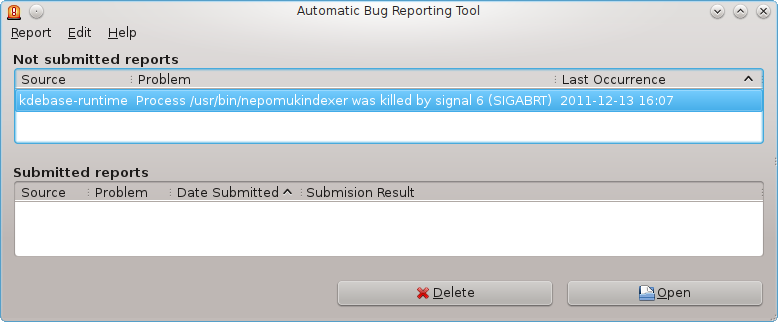
The installation image for Fedora 16 KDE is a Live CD, and while playing with the Live Desktop, Konqueror, the Web and file browser for KDE, crashed repeatedly. However, it has, so far, not crashed in the test installations used for this review. Other programs, however, have crashed. The bright side of applications crashing in Fedora 16 is that ABRT, the Automatic Bug Reporting Tool, makes it easy to report crash-prone applications to the developers.

The installed office application is KOffice (2.3.3), a native office application for KDE. If you have issues with using KOffice (it has been said that it does not open Microsoft documents properly), you can always install LibreOffice, which is in the repository.
CUPS, the printing service, is activated by default, but the system does not auto-configure or attempt to auto-configure connected printers. And if you attempt to configure one manually (using the printer setup utility), which is the only way to get a printer to work in Fedora 16, you might get the error message shown below. I think you will get this error if the user you are logged in as is not a member of the administrators group, or is not authorized to set up printers on the system. You will get a similar message if you attempt to configure a printer from CUPS’ Web interface, and you authenticate as a non-administrative user. You have to authenticate as root, if you want to setup a printer from the Web interface, which you can access by typing localhost:631 in any browser’s address bar.

systemd: Though systemd was first introduced in Fedora 15, nothing has been written about it on this website. And since it is a very important aspect of the system, here is some basic information about it. It is a system daemon. That is why it is called systemd, and it is a replacement for SysV init system. From the official page, systemd:
provides aggressive parallelization capabilities, uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services, offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux cgroups, supports snapshotting and restoring of the system state, maintains mount and automount points and implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic. It can work as a drop-in replacement for sysvinit.
With systemd, instead of managing system services and daemon with chkconfig, the command to use is systemctl. To enable NTP (Network Time Protocol), for example, you would use this command: systemctl enable chronyd.service. That starts it at boot time. To start it immediately, use: systemctl start chronyd.service. Chrony, by the way, is the NTP package in Fedora 16. It is a more advanced replacement for the ntp package, the NTP application in previous editions of Fedora.
Software Management Apper, the graphical application for managing software, appears to be the new name for “Get and Remove Software.” It is a KDE frontend for Packagekit. Out of the box, it is configured to check for updates daily.

And it enables you to queue applications for removal or installation, something that is not possible with Ubuntu‘s software Center and Linux Mint‘s Software Manager.

This screen shot shows part of the list of available updates on one of my test installations.

This is the part of a review where I usually write about the network and physical security features of a distribution, but since an article on the security features of Fedora 16 has been published separately, you may read it here.
Final Thoughts: With Fedora, you know what to expect on a default installation. You know that you will have to install some applications from a third party repository to get the system to just work. But there are certain aspects of the system which do not just work, and which have nothing to do with the project’s philosophical stance on software. Take printer configuration, for example. At this stage, I think connected printers should be auto-configured. Pardus, Linux Mint and other distributions have been doing it for some time.
Resources: Torrent and direct-download 32- and 64-bit Live CD images may be downloaded from here. Read other articles about Fedora on this website at its category page. Support questions may be posted here or on Questions & Answers.
Screen Shots: More screenshots from test installations of Fedora 16 KDE.
The default desktop showing Kickoff, the default menu style.

Components of KOffice, the installed office application, as viewed from the KDE Plasma Netbook interface.

Installed multimedia applications as seen from the KDE Plasma Netbook interface.





I have been wanting to check out the new version of Fedora, although I use XFCE and am not a big fan of KDE or Gnome. I am running 15, but haven’t had time to upgrade yet, although I think I may do it tonight.
Even though I am not traditionally a fan of KDE, it might be worth checking out again. It has been awhile since I tried it and it does look pretty spiffy in your screenshots. Might have to check out the live cd and, I suppose, give Gnome another chance too…
In the FWIW department, in order to get Amarok to play CDs it’s necessary to install the phonon-vlc backend. Gstreamer doesn’t work for some reason. In fact, I saw that the vlc backend was recommended on a KDE site.
With luxi fonts please . . .
Very good and technical review, but take note that Fedora 16 was officially released on November 8. Fedora is my favourite Linux distribution. It’s cutting edge, but, in the same time, I find it to be a stable and polished operative system (especially after the initial phase of upgrading). So far so good, no particular problems (right now I’m typing from F16 Gnome, but I use F16 KDE as well). No problems in printing with a printer connected via wireless (after installing the proprietary driver supplied by the hardware producer). Installing all the codecs and multimedia stuff is easy, but, obviously, you have to know the procedure. Anyway (for those who don’t know that) there are very good programs like autoplus or easy life that make very easy to install all the needed software. Long story short: I recommend it!
KDE’s far better than gnome and gnome shell. However, I don’t like KDE Fedora spin is loaded with trash from gnome. Because of this I’m using Kubuntu.
Nice review, as usual… Lots of pictures and descriptive text.
I liked Fedora KDE too… Until broke it.
If you’re interested, here are my reviews:
http://linuxblog.darkduck.com/2011/11/fedora-16-kde-improving-perfection.html – Live
http://linuxblog.darkduck.com/2011/11/fedora-16-kde-improving-perfection.html – installed version
I wonder why people bother to review a distro’s Live version.