GPT is an alternate disk partition table scheme that solves two issues associated with the MBR partition table scheme. It allows the configuration of more than four primary partitions, the maximum supported by MBR, and it also supports disk partitions of more than 2 TB.
Chakra, an Arch Linux-based distribution, is the only Linux distribution reviewed on this site that has out-of-the-box support for the GUID Partition Table, GPT. The only other distribution reviewed here with the same feature is PC-BSD (only available on release snapshots of PC-BSD 9).
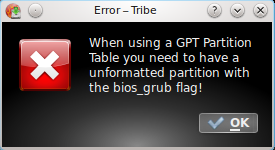
The key to setting up GPT-based partitions on Chakra is this. One of the partitions must have the bios_grub flag set. Without that, the installer will generate the error message shown in this image.

The rest of this article offers a guide on how to configure partitions on Chakra 2011.4, using a GPT scheme. The first step is to grab an ISO image of Chakra 2011.4, the latest stable release, bootup a computer from the resulting CD/DVD, and click until you get to the disk partitioning step. (a review of Chakra 2011.4 is available here.) Chakra’s installer is still a work in progress, and the installer does not have an automated partitioning feature: Disk partitions must be configured manually. To start, click on the Advanced button.

The installer uses the KDE partition Manager for disk partitioning. Select the disk you want to use and from the menu, click on Device > New Partition Table.

You have a choice of two partitioning schemes. The GPT, which we are going to use for this tutorial, and the MS-Dos or MBR, the traditional and default scheme. GPT will be pre-selected, so just click on Create New Partition Table.

Back on the main KDE partition Manager window, click on Apply to commit the change.

With the GPT partition table in place, time to start setting up the partitions. Part of the objective here is to show that with GPT, it is possible to create many more primary partitions than the maximum of four allowable under the MBR or MS-Dos scheme. For this test installation, five primary partitions, one each for /boot, /, /usr, Swap, and /home were configured. Before setting up these partitions, you must first configure an unformatted partition with the bios_grub flag set. To start, select the free space, and click on New.

The first partition must be unformatted, so for “File system,” select unformatted. The other property of this partition that must be specified is the size. Based on my experience, you can get away with the minimum allowed, which is 8 MB. Note that the “Partition type” will always be Primary. There are no extended or logical partitions in a GPT-based partition scheme.

With the first partition out of the way, select the free space, then click on New to create the next partition. Note that this will have to be repeated for all the other partitions.




i have been using ubuntu since 7.10 and mint the last 2 years. i have been trying install chakra for 3 days now and the level of fucked up programming on the partition and disk setup is beyond anything i have seen before ( including windows )
i insanely love the look and feel of chakra using it on live boot so my frustration in not being able to do a simple install ( i’m not a noob at this ) makes me want to throw my computer out the window.
i will not look at or attempt to use this os again. good luck
Well, I agree with you. I don’t get it how in these times Distro is not capable of easy and “stupid simple” install. Now I Know why is Chakra less popular than other distros. Manjaro is Arch based distro with beta graphic installer and it still works better. Click, entire disk, automatic, install.. finished. I am Linux user for fifth year and i Didn’t know what the hell is GPT and how to do it. New or less experienced user just install something easy and the other users will be using Arch with more funcionalities. Chakra Team needs to make decision which way are they going, because now, it’s just not for BFU and even not for hard tech linux users. But I wish them everything good, clean qt/KDE distro forked from arch is something nice…