To create a custom rule, click on the Add button on the main Gufw window. The rule creation window has three tabs – Preconfigured, Simple and Advanced. From the Preconfigured, you can create very broad rules for a preset number of applications and services. The preset services are: FTP, HTTP, IMAP, NFS, POP3, Samba, SMTP, ssh, VNC and Zeroconf, and the preset applications or programs are: Amule, Deluge, KTorrent, Nicotine, qBittorrent, and Transmission.
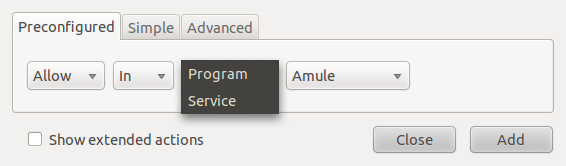
Preconfigured rules
The Simple tab allows you to create rules with a port number defined. This makes it possible to create rules for services and applications not preset in the Preconfigured tab.
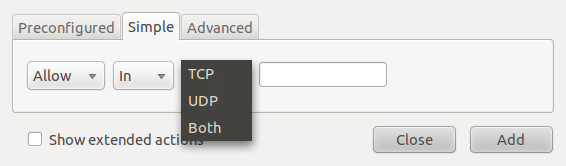
Gufw's simple rules creation interface
The Advanced tab makes it possible to create more specific rules using source and destinations ports and addresses.
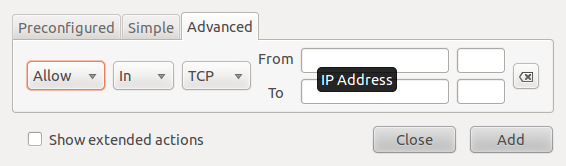
Gufw's advanced rules creation interface
The example below creates a rule from the Preconfigured tab allowing ssh traffic into a host. While this makes it easy for anybody to create a firewall rule, it lacks specificity. In this example, ssh traffic from all sources would be allowed in. That’s not a good thing, unless that is what you want.
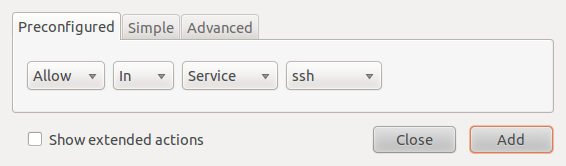
Using pre-configured services
Once a rule has been created, it will be shown in the main window of Gufw. You may also view the rule from a shell terminal by typing sudo ufw status.
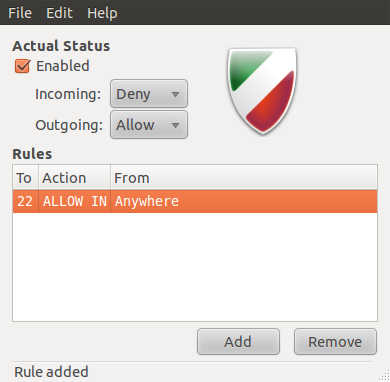
Generated rules in the main Gufw window
This second example shows how to create a rule from the Simple tab. The example shown in the image below is for a rule allowing ssh traffic in to the host.
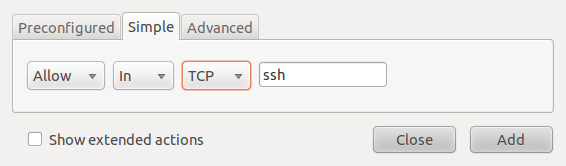
Creating rules in the Simple tab
Rather than use a service or application name, you could just specify the port number associated with that application or service. To repeat the ssh rule in the example above using a port number, you would specify port 22, which is the default port for ssh.
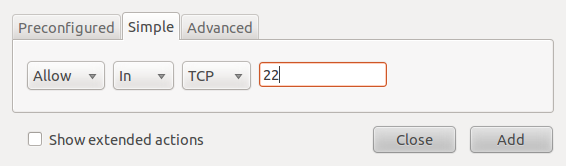
Simple rule creation with port number
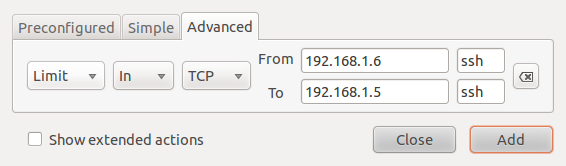
This example shows how to create a rule from the Advanced tab. The rule shown in the image below allows ssh traffic from all hosts in a network to a particular host in another network. Note: The IP addresses used in these rules do not represent addresses used in a real case.
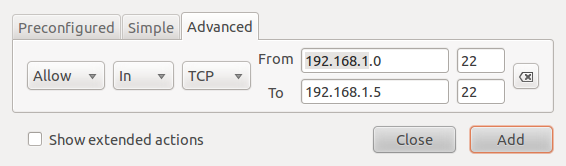
Advanced rule creation
What if you want to create a rule to allow IPsec VPN traffic. First, you need to know the port numbers involved in an IPsec conversation. These would be port 50 for the Encapsulating Security Payload (esp), and port 51 for the Authentication Header (ah). Thus to create the rule for esp, you would use the port number as shown below.

To create a rule for the Authentication Header, you would specify port 51.