 How to dual-boot Windows 7 and Debian 6 is the latest in the series of articles on dual-booting Windows 7 and Linux and BSD distributions. None has been written for a BSD distribution, but with PC-BSD 8.2 scheduled to be released early next week, expect one to be written for it.
How to dual-boot Windows 7 and Debian 6 is the latest in the series of articles on dual-booting Windows 7 and Linux and BSD distributions. None has been written for a BSD distribution, but with PC-BSD 8.2 scheduled to be released early next week, expect one to be written for it.
When attempting to dual-boot Windows and a Linux or BSD distribution, one of the most important decisions you will have to make is where to install the bootloader. You can install it in the Master Boot Record (MBR) of the hard disk, or in the boot partition of the Linux or BSD installation.
Because upgrading Windows tends to overwrite the boot loader, if it is installed in the MBR, the best location for installing the bootloader is the boot partition or, if you are installing to a second hard disk, the MBR of the second hard disk. Doing that will ensure that nothing you do on Windows will affect the Linux or BSD installation.
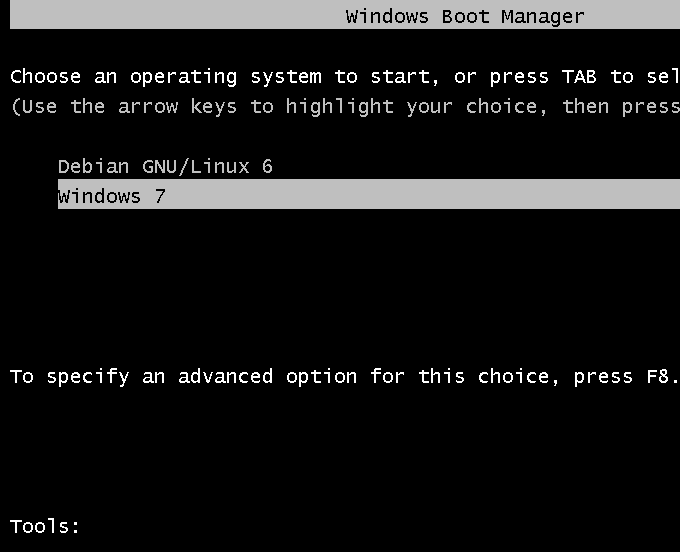
If you follow the recommended method, you will always be presented with the Windows boot menu any time you (re)boot the computer. You may then boot into Windows or Debian. You will still have access to GRUB’s boot menu.

Note: This tutorial assumes installation on a computer with a single hard drive, and an existing installation of Windows 7. If you are installing a fresh copy of Windows, it is best to leave some free space, enough to install Debian.
To begin, download a suitable installation of Debian 6. If you need help choosing, read Debian 6 installation and disk partitioning guide.
To reduce reduce the number of images used, this tutorial begins at the step where disk detection starts. Select “Manual.” Continue.

Here, the installer shows existing NTFS partitions. As you can see, there is no free, or unallocated space. In order to install Debian 6, therefore, it will be necessary to resize /dev/sda2, the main Windows partition. To do that, scroll to that partition and double-click it, or highlight it and click Continue.

Scroll to “Resize partition …” Continue.

This is true size of the partition. The installer tells you the upper and lower limit that you can go.

For this tutorial, I decided that 100 GB is all I need for the Windows partition. Continue.

Now that there is free space, we can now proceed to partition that space for Debian 6. Select it, then click Continue.

Scroll to “Create a new partition.” Continue.

By default the /boot partition on Debian 6 is allocated a disk space of about 250 MB. Most Linux distributions use 500 MB. I think 250 MB will do just fine. Continue.





Very, very useful tut. Thanks!
Hi, thanks for this simple and practic explanation. Last night I did this step by step and when I was asked to reboot, the message “grub rescue unknown files” appeared. Now, I’m not really sure what this means.
As I said, I followed step by step this tutorial and installed grub on /boot. Can you help me out?
Thanks!